Integrating MuleSoft with RPA and IDP for Business Automation
11/22/2025
Modern enterprises face a critical challenge: processing thousands of documents daily while maintaining accuracy, speed, and compliance. The integration of MuleSoft's Anypoint Platform with Robotic Process Automation and Intelligent Document Processing creates a powerful automation solution that transforms document-heavy workflows into streamlined digital processes.
The Integration Architecture
API-Led Connectivity as the Foundation
MuleSoft's API-led connectivity approach provides the architectural backbone for integrating RPA and IDP. This three-layer architecture—System, Process, and Experience APIs—enables reusable, scalable integrations. System APIs unlock data from backend systems, Process APIs orchestrate business logic combining RPA and IDP capabilities, and Experience APIs deliver optimized interfaces for different channels.
API connectivity: a tiered model with Experience, Process, and System APIs
This layered approach ensures that when RPA bots execute document processing workflows, they consume standardized APIs rather than brittle point-to-point connections. The result is automation that scales reliably across the enterprise.
The Automation Synergy
Integrating these technologies creates capabilities exceeding what each achieves independently. IDP extracts data from unstructured documents using AI-powered recognition, RPA orchestrates workflows across multiple systems, and MuleSoft's platform connects everything to enterprise applications. This synergy automates end-to-end processes from document intake through data extraction to system updates.
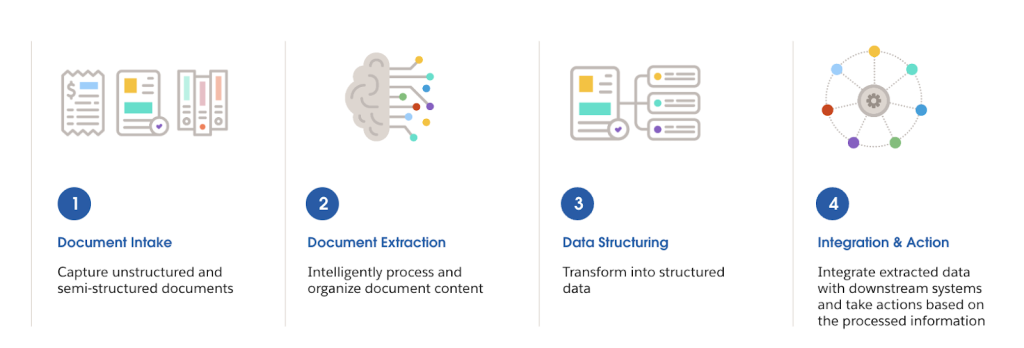
Technical Implementation
Step 1: Creating Document Actions
Document actions are AI models trained to extract data from specific document types like invoices, purchase orders, or contracts. In MuleSoft IDP, users create document actions by selecting templates for common documents or configuring custom models for unique formats. The configuration defines fields to extract—invoice numbers, dates, amounts, customer names—and the AI learns to locate these across varying layouts.
Once configured and tested, document actions are published to Anypoint Exchange, making them available as APIs for RPA consumption. This publication exposes POST endpoints to submit documents and GET endpoints to retrieve extraction results.
Step 2: Configuring Connected Apps
Secure integration requires creating a connected app in Anypoint Platform's Access Management with the "Execute Published Actions" scope. This generates Client ID and Client Secret credentials that RPA bots use for authentication. Users executing document actions also need the "Execute Published Actions" permission.
Step 3: Building RPA Workflows
MuleSoft RPA Builder provides two specialized actions for IDP integration:
Submit Document to MuleSoft IDP browses published document actions, accepts the file path, and submits documents for processing. The action immediately returns an execution ID for tracking.
Retrieve Results from MuleSoft IDP queries execution status using the execution ID. Since processing is asynchronous, results may not be immediately available.
Step 4: Implementing Retry Logic
Production implementations incorporate retry mechanisms because document processing takes time. A typical pattern creates a loop that checks status, waits 20 seconds if processing continues, and retries up to three times. The RPA workflow uses a managed block with do-action, on-error, and do-always scopes for comprehensive error handling.
Status responses include "in progress," "completed," or "manual validation required" when confidence scores fall below thresholds. For manual review cases, business users access the IDP review interface to validate and correct extracted data before proceeding.
Step 5: Processing Extracted Data
When processing completes, the retrieve action returns extracted data as JSON. RPA bots parse this data and use it in downstream steps—writing to Excel spreadsheets, updating databases, populating CRM fields, or triggering approval workflows. The structured output format ensures consistency across executions.
Real-World Applications
Healthcare Document Processing
A diagnostic testing company implemented this integration to automate their Laboratory Information Management System workflows. The solution processes 15,000 samples daily, saving over 100,000 hours annually and realizing approximately $4 million in cost savings. The automation captures data from incoming sample requests, validates information, and streamlines processing.
Financial Services Automation
Invoice processing workflows extract vendor information, line items, amounts, and payment terms from diverse invoice formats. The system validates extracted data against purchase orders and business rules before routing for approval. This accelerates accounts payable cycles, improves vendor relationships, and maintains accurate financial records.
Insurance Claims
Claims processing extracts information from diverse documents including claim forms, medical records, police reports, and supporting evidence. The technology automatically classifies documents by type, extracts relevant details, and validates information against policy terms. Automated claims processing reduces cycle times from days to hours while improving accuracy.
Business Benefits
Operational Efficiency
Automating document extraction and processing reduces handling time from hours to minutes. Organizations report processing thousands of additional documents daily with existing staff levels. The speed improvement cascades through dependent processes, accelerating everything from order fulfillment to customer onboarding.
Enhanced Accuracy
AI-powered extraction with validation achieves significantly higher accuracy than manual data entry while maintaining consistent performance regardless of volume. Organizations reduce error rates by 70-90%, improving data quality for analytics and ensuring regulatory compliance.
Scalability
Automated workflows handle volume fluctuations without proportional resource additions. Organizations process seasonal peaks and sustained growth using existing automation infrastructure. Technology scaling costs remain far below hiring and training additional staff.
Cost Reduction
Processing cost per document drops dramatically with automation. Beyond direct labor savings, organizations benefit from faster processing reducing working capital requirements, improved accuracy preventing costly corrections, and scalability avoiding hiring costs.
Accelerated Time to Value
Pre-built document action templates for common document types enable rapid deployment without building extraction logic from scratch. Business users can create automations with minimal IT involvement, reducing deployment timelines.
Implementation Considerations
Document Variability
Real-world documents arrive in inconsistent formats and varying quality levels. Organizations address this through preprocessing that enhances image quality and training AI models with diverse examples. Implementing confidence thresholds and human-in-the-loop review for uncertain extractions balances automation with accuracy.
Security and Compliance
Automation workflows accessing sensitive data require robust security controls. Connected apps provide secure authentication without sharing individual passwords. Role-based access control limits permissions to required actions. Encrypting credentials, implementing rotation schedules, and maintaining audit logs strengthen security posture.
Monitoring and Governance
Production automation requires visibility into execution status, performance metrics, and error conditions. Monitoring dashboards display documents processed, success rates, processing times, and error patterns. Establishing governance standards for document action creation, API design, and error handling promotes consistency across initiatives.
Change Management
Technology implementation succeeds only when people embrace new processes. Effective change management communicates how automation eliminates tedious work enabling staff to focus on higher-value activities. Training programs build skills and confidence using new tools.
Resource Consumption Model
MuleSoft packages automation capabilities through Automation Credits covering Integration, IDP, RPA, Composer, and Flow Orchestration. RPA consumes credits per minute of bot execution time, while IDP consumes credits per page processed. This flexible model allows organizations to allocate resources toward tools delivering the most value.
Conclusion
Integrating MuleSoft with RPA and IDP delivers comprehensive business automation that transforms document-intensive processes. The combination of API-led connectivity, robotic process automation, and intelligent document processing creates end-to-end workflows that improve efficiency, accuracy, and scalability while reducing costs. Organizations implementing this integration position themselves to respond quickly to changing business requirements while maintaining operational excellence.
References and Further Reading
MuleSoft Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) Solution